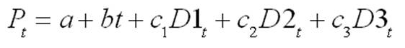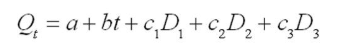ECO6214: Module 7: Exam II | Attempt 1 | Score for this quiz: 150 out of 150 ...
ECO6214: Module 7: Exam II
Score for this quiz: 150 out of 150
Submitted May 1 at 2:13am
This attempt took 55 minutes.
Question 1 10 / 10 pts
The linear regression equation, Y = a + bX, was estimated. The following computer printout was obtained:
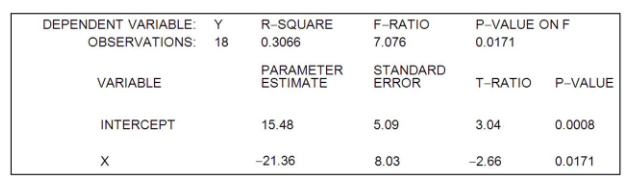
The parameter estimate of a indicates
- when X is zero, Y is 15.48
- when Y is zero, X is 8.03
- when Y is zero, X is -21.36
- when X is zero, Y is 5.09.
Question 2 10 / 10 pts
The linear regression equation, C = a + bQ+cQ, was estimated. The following computer printout was obtained:
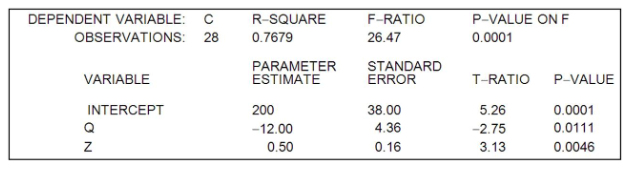
The value of R2 indicates that _______ of the total variation in C is explained by the regression equation.
- 7.679%
- 76.79%
- 7679%
- 0.7679%
Question 3 10 / 10 pts
The manufacturer of Beanie Baby dolls used quarterly price data for 2005I-2013IV (t = 1, ..., 36) and the regression equation:
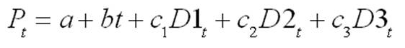
to forecast doll prices in the year 2014. Pt is the quarterly price of dolls, and, and are dummy variables for quarters I, II, and III, respectively.
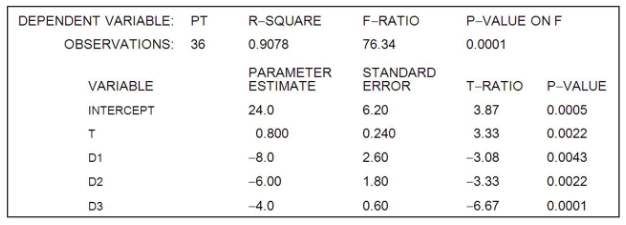
What is the estimated intercept of the trend line in the 3th quarter?
Question 4 10 / 10 pts
A forecaster used the regression equation
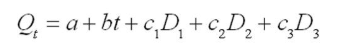
and quarterly sales data for 1996I-2013IV (t = 1, ..., 64) for an appliance manufacturer to obtain the results shown below. Q is quarterly sales, and , and are dummy variables for quarters I, II, and III.
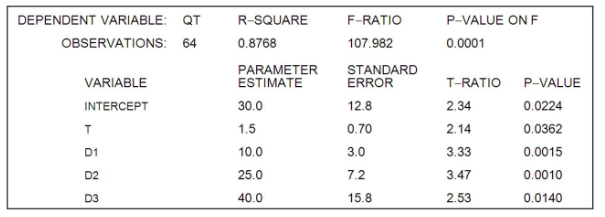
Using a 5 percent significance level, these estimation results indicate that
- sales in the fourth quarter are significantly greater than sales in any other quarter.
- sales in the third quarter are significantly greater than sales in any other quarter.
- sales in the second quarter are significantly greater than sales in any other quarter.
- sales in the first quarter are significantly greater than sales in any other quarter.
Question 5 10 / 10 pts
When the correlation coefficient is negative, it means:
- when X goes down, Y does too.
- Y will not be a good predictor of X.
- X will not be a good predictor of Y.
- when X goes down, Y tends to go up.
- there is a weak relationship.
Question 6 10 / 10 pts
Thirty data points on Y and X are employed to estimate the parameters in the linear relation Y = a + bX. The computer output from the regression analysis is:
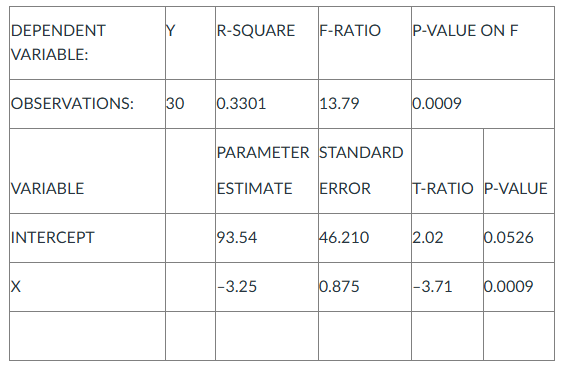
The parameter estimate of a (intercept) indicates
- when Y is zero, X is -3.25.
- when Y is zero, X is 93.54.
- when X is zero, Y is -3.25.
- when X is zero, Y is 93.54.
Question 7 10 / 10 pts
The linear regression equation, Y = a + bX, was estimated. The following computer printout was
obtained:
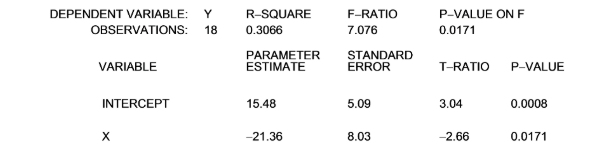
Given the above information, which of the following statements is correct at the 1% level of significance?
- â (intercept) is statistically significant, but (slope) is not
- Both â(intercept) and (slope) are statistically significant.
- (slope) is statistically significant, but â (intercept) is not.
- Neither â intercept) nor (slope) is statistically significant.
Question 8 10 / 10 pts
The linear regression equation, Y = a + bX, was estimated. The following computer printout was
obtained:

Given the above information, if X equals 20, what is the predicted value of Y?
- -411.72
- 186.42
- -186.42
- 165.69
Question 9 10 / 10 pts
A forecaster used the regression equation
Qt = a + bt +c1D1 +c2D2 + c3D3
and quarterly sales data for 1996I-2013IV (t = 1, ..., 64) for an appliance manufacturer to obtain the results shown below. Q is quarterly sales, and D1,D2 and D3 are dummy variables for quarters I, II, and III.
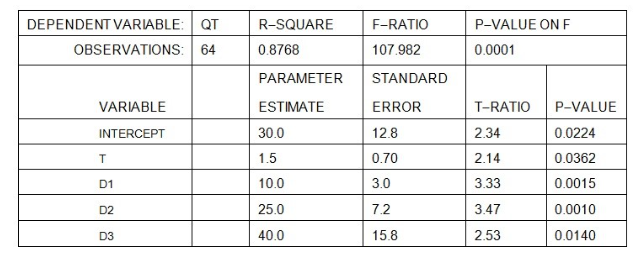
What is the estimated intercept of the trend line in the second quarter?
Question 10 10 / 10 pts
A forecaster used the regression equation
Qt = a + bt +c1D1 +c2D2 + c3D3
and quarterly sales data for 1996I-2013IV (t = 1, ..., 64) for an appliance manufacturer to obtain the results shown below. Q is quarterly sales, and D1,D2 and D3 are dummy variables for quarters I, II, and III.

At the 5 percent level of significance, is there a statistically significant trend in sales?
- Yes, because 2.14 >0.05.
- No, because 1.5 > 0.05.
- Yes, because 0.700 > 0.05.
- Yes, because 0.0362 < 0.05
Question 11 10 / 10 pts
A firm is experiencing theft problems at its warehouse. A consultant to the firm believes that the dollar loss from theft each week (T) depends on the number of security guards (G) and on the unemployment rate in the county where the warehouse is located (U measured as a percent). In order to test this hypothesis, the consultant estimated the regression equation T = a + bG + cU and obtained the following results:
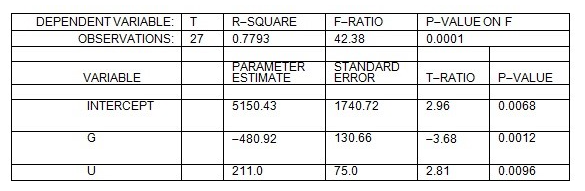
Based on the above information, hiring one more guard per week will decrease the losses due to theft at the warehouse by _________ per week.
Question 12 10 / 10 pts
For the equation Y = a + bX, the objective of regression analysis is to
- estimate the variables Y and X.
- estimate the parameters a and b.
Question 13 10 / 10 pts
In a linear regression equation of the form Y = a + bX, the intercept parameter b shows
- the increase in the value of X when Y increases by 1 unit.
- the increase in the value of Y when X increases by 1 unit.
Question 14 10 / 10 pts
If an analyst believes that more than one explanatory variable explains the variation in the dependent variable, what model should be used?
- a multiple regression model
- binary model
- a simple linear regression model
- quadratic model
Question 15 10 / 10 pts
Income is used to predict savings. For the regression equation Y = 1,000 + .10X, which of the following is true?
- Y is income, X is savings, and income is the independent variable.
- Y is income, X is savings, and savings is the independent variable.
- Y is savings, X is income, and income is the independent variable.
- Y is savings, X is income, and savings is the independent variable.